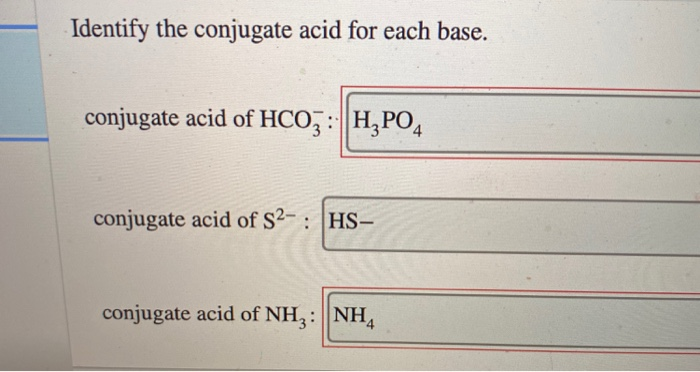
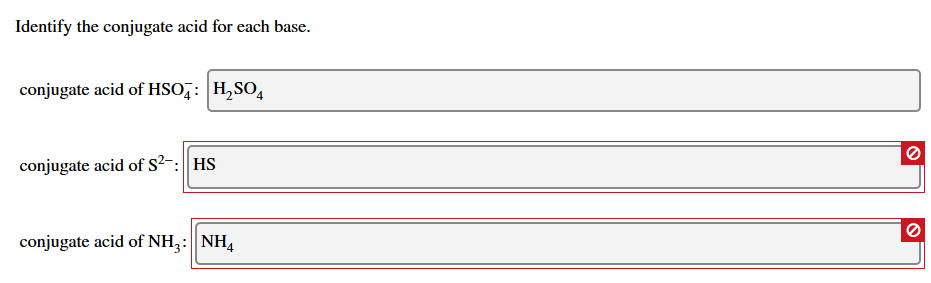
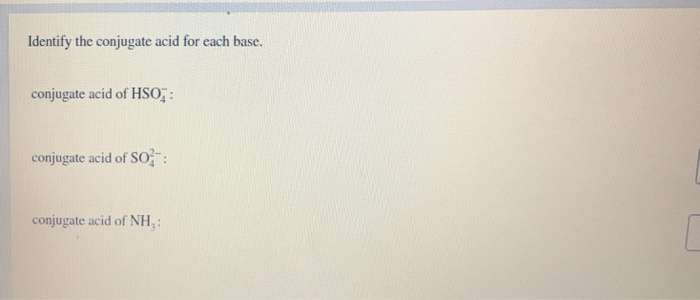
Identify the Conjugate Acid for Each Base
To identify the strongest base we can determine their weakest conjugate acid. Identify the acid-base conjugate pairs for pyridine.

Solved Identify The Conjugate Acid For Each Base Conjugate Chegg Com
HCl H2O Cl- H3O arrow_forward Determine the acidbase conjugate base and conjugate acid in the following reaction.
. The H₂O becomes OH. If you are given an acid and want to find the conjugate base just remove an H from the formula. Base B- rightleftharpoons Conj.
Conjugate acid of PO34. Identify the conjugate acid for each base. Or we can say.
H 2 SO 4. The conjugate acids of CH 3 NH 2 and S 2 are CH4 NH3 and HS respectively. See the equation for two conjugate pairs A and B.
Conjugate base is NH 3. For the Following reactions identify the acidbase and conjugate acidBase pairs. Next we consider that acidity increases with positive charge on the molecule thus ruling out that S 2 is the weakest base.
Conjugate base is HPO 4 2-NH 4. Up to 25 cash back 1HCO3- is the conjugate acid CO32- is the conjugate base. The acid HCOOH f.
Conjugate base is HSO 4-H 2 PO 4-. The conjugate acid-base pairs are HCNCN and HNO2NO2 3. Thus for the ionization of HCl HCl is the conjugate acid and Cl is the conjugate base.
We also have water and hydronium which are also related by that one H plus. CH3COOH CO32- -- CH3COO- HCO3-. In this case we have HF and F minus that are related to each other by that one H plus.
So Conjugate acid of HSO 4- is H 2 SO 4. HClO4 HClO4 -- H ClO4-. The conjugate acid-base pairs are H2CO3HCO3 and H3OH2O.
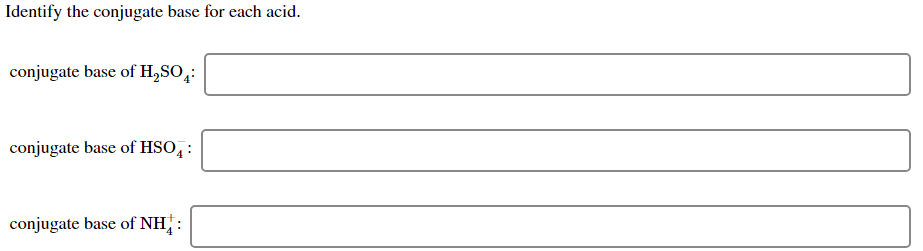
B At 25 C what is the hydroxide ion concentration OH in an aqueous solution with a hydrogen ion concentration. A Identify the conjugate base for each acid. A BrO- or ClO-.
And so HF and F minus are a conjugate acid-base pair. So OH is the conjugate base of H₂O. HCO₃ H₂O H₂CO₃ OH base acid Conj A Conj B.
The conjugate acid-base pairs are HFF and d HCHO2CHO 2. A and are conjugate acid and base respectively. The conjugate base of any BL acid is simply that acid less a proton H.
Acid HA Conj. For this reason different conjugate pairs often react in pairs. The base NH3 d.
Conjugate base of H2S. HCl aq H 2 O H 3 O aq Cl aq In the discussion of Brønsted acid-base behavior the hydrogen atom that is transferred is generally referred to as a proton because it is transferred as a hydrogen atom without its electron. Identify the acid base conjugate acid and conjugate base in the following equation.
The acid HNO3 e. We see that HCO₃ becomes H₂CO₃. Conjugate acid of NH3.
You will see which is the acid and which the base because the roles are reversed in the products. Please check this question. The base KOH c.
List the conjugate acid or conjugate base for each chemical. A conjugate acid contains one more H atom and one more charge than the base that formed it. Identify the conjugate acid for each base.
A conjugate base contains one less H atom and one more - charge than the acid that formed it. So water and H3O plus are also a conjugate acid-base pair. Conjugate acid of NH3.
Conjugate base of NH4. It has one more H atom and one more charge -1 1 0. Drawing Cyclohexane Rings Organic Chemistry.
Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs Ordered by Strength Acids Bases strong weak HClO 4 ClO 4 H 2SO 4 HSO 4 HCl Cl HNO 3 NO 3 H 3O H 2O H 2C 2O 4 oxalic acid HC 2O 4 H 2SO 3 SO 2aq H 2O HSO 3 HSO 4 SO 4 2 HNO 2 NO 2 HF F HCO 2H formic acid HCO 2 C 6H 5CO 2H benzoic acid C 6H 5CO 2 HC 2O 4. B and are conjugate acid and base respectively. Conjugate acid of SO 4-2 is HSO 4-.
Conjugate acid of HSO4. If you begin with a base and want to find the conjugate acid just add an H to the formula. So H₂CO₃ is the conjugate acid of HCO₃.
HCO₃ H₂O H₂CO₃ OH. Base acid Conj A Conj B. TABLE OF CONJUGATE ACID-BASE PAIRS Acid Base K a 25 oC HClO 4 ClO 4 H 2 SO 4 HSO 4 HCl Cl HNO 3 NO 3 H 3 O H 2 O H 2 CrO 4 HCrO 4 18 x 101 H 2 C 2 O 4 oxalic acid HC 2 O 4 590 x 102 H 2 SO 3 SO 2 aq H 2 O HSO 3 171 x 102 HSO 4 SO 4 2 120 x 102 H 3 PO 4 H 2 PO 4 752 x 103 FeH 2 O 6 3 FeH 2 O 5 OH 2 184 x 103 H 2 C 8 H.
The acid HF b. In this equation HClO4 has donated a proton to H2O so HClO4 is acting as an acid and as H2O is accepting a proton so H2O is a baseClO4- on the other side can accept a proton so ClO4- is a base but its a conjugate base to acid HClO4 since it is generatd by losing a proton from HClO4 Similary H3O is an acid as it can donate a proton but it is. Alkanes and Alkenes Organic Chemistry.
According to the Bronsted Lowry concept Bronsted Lowry-acid is a substance that donates one or more hydrogen ion in a reaction and Bronsted Lowry-base is a substance that accepts one or more hydrogen ion in a reaction. Conjugate acid of NH 3 is NH 4. Conjugate base of H2PO4.
Let us take the example of bicarbonate ions reacting with water to create carbonic acid and hydronium ions. It has one less H atom and one more charge. Conjugate acid of S2.
Indicate the appropriate chemical name for each of the following structures. Conjugate acid of H2PO4. Conjugate acid is formed by adding an H ion to the given base.
2Conjugate acid of HPO42-- H2PO4-. HCl H2O H3O Cl- HSO4- HClO4 H2SO4 ClO4- NH3 CH3- CH4 NH2- arrow_forward Based on their compositions and structures and on conjugate acidbase relationships select the stronger base in each of the following pairs.

Solved Identify The Conjugate Acid For Each Base Conjugate Chegg Com
Solved Identify The Conjugate Acid For Each Base Conjugate Chegg Com
Solved Identify The Conjugate Acid For Each Base Conjugate Chegg Com
Solved Identify The Conjugate Base For Each Acid Conjugate Chegg Com
Comments
Post a Comment